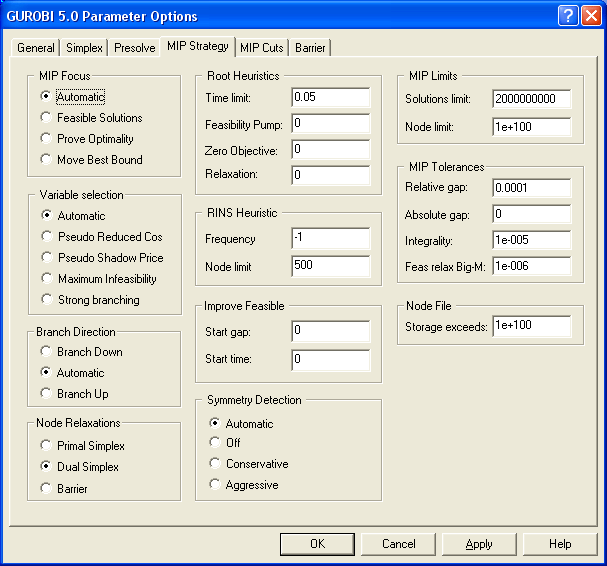
Figure 4.64: The MIP Strategy Tab in the GUROBI Options Dialog Box
You can change the Simplex options for GUROBI by choosing GUROBI parameters from the Options menu and then pressing the Simplex tab. This will display the dialog box shown below:

Figure 4.64: The MIP Strategy Tab in the GUROBI Options Dialog Box
| Option Name | MPL Name | Solver Param | ParamNr | Type | Default | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIP Focus | MipEmphasis | MIPFOCUS | 54 | list | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Variable Selection | MipVariableSelect | VARBRANCH | 22 | list | -1 | -1 | 3 |
| Branch Direction | MipBranchDir | BRANCHDIR | 70 | list | -1 | -1 | 1 |
| Node Relaxations | MipRootMethod | NODEMETHOD | 33 | list | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Root Heuristic Time limit | MipHeuristic | HEURISTIC | 20 | real | 0.05 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Feasibilty Pump | MipPumpPasses | PUMPPASSES | 55 | int | 0 | 0.0 | maxint |
| Zero Objective | MipZeroObjNodes | ZEROOBJNODES | 36 | int | 0 | 0.0 | maxint |
| MinRelaxtion Heuristic | MinNodesRelHeur | MINRELNODES | 71 | int | 0 | 0 | maxint |
| RINS Frequency | MipRINSFreq | RINS | 68 | int | 500 | 0 | MAXINT |
| RINS Node Limit | MipRINSNodeLimit | SUBMIPNODES | 21 | int | 500 | 0 | MAXINT |
| Improve Start Gap | MipImproveStartGap | IMPROVESTARTGAP | 30 | real | 0.0 | 0.0 | MAXREAL |
| Improve Start Time | MipImproveStartTime | IMPROVESTARTTIME | 31 | real | MAXREAL | 0.0 | MAXREAL |
| Symmetry Detectiion | MipSymmetry | SYMMETRY | 57 | list | -1 | -1 | 2 |
| Solution Limit | MipSolutionLimit | SOLUTIONLIMIT | 17 | int | 1 | 1 | MAXINT |
| MIP Node Limit | MipNodeLimit | NODELIMIT | 16 | real | MAXREAL | 0.0 | MAXREAL |
| MIP Relative Gap Tolerance | MipRelativeGap | MIPGAP | 19 | real | 1e-4 | 0.0 | MAXREAL |
| MIP Absolute Gap Tolerance | MipAbsoluteGap | MIPGAPABS | 56 | real | 1e-10 | 0.0 | MAXREAL |
| Integrality Tolerance | MipIntegerTol | INTFEASTOL | 18 | real | 1e-5 | 1e-9 | 0.1 |
| Feas relax Big-M Tolerance | MipFeasRelaxBigM | FEASRELAXBIGM | 51 | real | 1e6 | 0 | MAXREAL |
| Node Storage Exceeds | MipNodefileStart | NODEFILESTART | 32 | real | MAXREAL | 0.0 | MAXREAL |
Determines the focus of the solve.
| Automatic (0) | Balances between finding feasibile solutions and proving optimality. |
| Feasible Solutions (1) | Focuses on finding feasible solutions. |
| Prove Optimality (2) | Focuses on proving optimality. |
| Move Best Bound (3) | Focuses on improving the best bound. |
Controls the branch variable selection strategy.
| Automatic (-1) | GUROBI decides. |
| Pseudo Reduced Cost (0) | Available alternatives are Pseudo Reduced Cost Branching. |
| Pseudo Shadow Price (1) | Pseudo Shadow Price Branching. |
| Maximum Infeasibility (2) | Maximum Infeasibility Branching. |
| Strong Branching (3) | Strong Branching. |
Controls the branch variable selection strategy.
| Branch Down (-1) | Explores down the branch first. |
| Automatic (0) | Automaticall choosen. |
| Branch Up (1) | Explores up the branch first. |
Controls the algorithm used for MIP node relaxations.
| Primal Simplex (0) | Uses Primal Simplex. |
| Dual Simplex (1) | Uses Dual Simplex. |
| Barrier (2) | Uses Barrier. |
Controls the amount of time spent in MIP heuristics. Larger values produce more and better feasible solutions, at a cost of slower progress in the best bound.
Sets the number of passes the feasiblity pump performs.
Sets the number of passes the feasiblity pump performs.
Sets the number of nodes to explore in the Minimum Relaxation Huerisitic..
Sets the frequency of the RINS hueristics. Default value (-1) chooses automatically, a value of 0 turns off RINS, a positive value n performs RINS every n-th node of the MIP search tree.
Limits the number of nodes explored by the RINS heuristic. Exploring more nodes can produce better solutions, but it generally takes longer.
The MIP solver can change parameter settings in the middle of the search, moving away from best bound and devotes efforts on finding feasible solutions. This paramter specifies the optimality gap at which the MIP solver will switch to this strategy.
The MIP solver can change parameter settings in the middle of the search, moving away from best bound and devotes efforts on finding feasible solutions. This paramter specifies the time in seconds which the MIP solver will switch to this strategy.
Controls the MIP symmetry detection.
| Automatic (-1) | Chooses Automatically. |
| Off (0) | No detection method used. |
| Conservative (1) | Moderate level of detection. |
| Aggressive (2) | Aggressive level of detection. |
Limits the number of feasible solutions found (MIP only).
Limits the number of MIP nodes explored (MIP only).
Relative MIP optimality gap (MIP only). The MIP engine will terminate (with an optimal result) when the gap between the lower and upper objective bound is less than MIP Relative Gap Tolerance times the upper bound.
Absolute MIP optimality gap (MIP only). The MIP engine will terminate (with an optimal result) when the gap between the lower and upper objective bound is less than MIP Absolute Gap Tolerance.
Integer feasibility tolerance (MIP only). An integrality restriction on a variable is considered satisfied when the variable's value is less than Integrality Tolerance from the nearest integer value.
When relaxing a constraint in a feasibility relaxation, it is sometimes necessary to introduce a big-M value. This parameter determines the default magnitude of that value.
Controls the point at which MIP tree nodes are written to disk. Whenever the node storage exceeds the specified value (in GBytes) are written to disk.